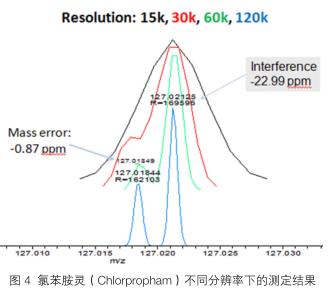
Peng Xing 1 , Zhu Manjie 1 , Li Chunli 1 , Reed 2 Abstract <br>In this study, a precise mass database of 435 pesticide compounds was established by gas chromatography-quadrupole-electrostatic orbital high resolution mass spectrometry (Thermo ScientificTM Q Exactive-GC), and combined with the corresponding data processing software. Based on the rapid screening process for pesticide residues. The experiment optimizes the parameters required for the search to improve the screening accuracy and avoid false positive and false negative results. The experimental results show that in the actual sample detection, the resolution of 60,000 FWHM (200 m / z) and above, the mass accuracy < 2.0 ppm, the screening accuracy will be greatly improved. At the same time, it can still maintain high sensitivity and fully meet the pesticide residue detection requirements in food. The screening method uses both accurate mass and deviation, retention time window, isotope distribution and isotope abundance information to obtain fast and accurate results. 3.2.3 Ultra-high resolution performance When there is matrix interference, the resolution will affect the measurement of accurate quality. Ultra-high resolution improves the accuracy of the instrument's accurate mass measurement and allows for the identification of compounds with extremely close precision. In the experiment, the results of the 10 μg/L Chlorpropham fragment ion (m/127.01833) in the onion samples were obtained at four different resolutions (15,000; 30,000; 60,000; 120,000). At 60,000, the ions cannot separate from the interfering ions of the same weight element. Therefore, a false negative or false positive result will occur in the judgment. Only when the resolution is 60,000 and above, the two isobaric ions can be clearly distinguished, and the chloroaniline can be quickly judged and accurately quantified, as shown in Fig. 4. 3.2.4 Superior anti-interference ability The experiment also examines the high-resolution and high-quality precision of Q Exactive-GC for a relatively complex matrix, achieving perfect chromatographic separation with accurate mass. As shown in Figure 5, high quality chromatographic peaks were obtained at low concentrations (10.0 μg/L) in the tobacco matrix. 3.3 Establishment of the database (Database) <br> This experiment selected 435 pesticide compounds, prepared into a 2.0 mg / L mixed standard solution, determined by the instrument, in the full scan mode (FullScan) to obtain the retention time of the corresponding compound , the precise molecular weight of the fragment ions, chemical formula and other information. Select 2-5 fragment ions for each compound to obtain ion information (precise mass, chemical formula). The data is imported into TraceFinder to create a related database (Database). As shown in Figure 6. TraceFinder not only enables fast, batch, and automated processing of data, but also integrates qualitative, quantitative, and method-based functions. Based on the established Database, Targeted Screening can be used to quickly screen pesticide residues in test samples. The Database mainly contains information such as compound name, CAS registration number, fragment ion information (precise quality, chemical formula), retention time, and so on. 3.4 Optimization of screening parameters <br> Retention time is the characteristic parameter of the compound under chromatographic conditions. For this experiment, qualitative mainly depends on the exact mass, but at the same time, the retention time limit can effectively reduce the detection of false positive results and improve the accuracy and speed of screening. Trace1310 Gas Chromatography is highly stable, ensuring compound retention time stability. For multiple determinations, the retention time deviation of the same compound was within ±0.1 min. Considering the offset of matrix interference on retention time, the experiment set the retention time deviation within ±0.2 min. The isotope cluster information possessed by the compound is important for qualitative analysis. For the pesticide compounds in this study, the elemental composition is mainly C, H, O, N, P, S, F, Cl, Br, I, of which C, S The isotopic contributions of Cl, Br are more than 1.0%, especially the isotopic contributions of Cl and Br account for 32.0% and 97.3%, and the isotope contribution increases with the increase of the number of elements in the compound. 3.5 Screening Results <br> This experiment was conducted with a solvent standard and a matrix standard to verify the pesticide compound database. Two common fruit and vegetable samples (apples and cucumbers) were selected. The results showed that 435 compounds were detectable at a concentration of 10.0 μg/kg. All pesticides can be qualitatively detected under standard (10.0 μg/kg), and the sensitivity of the method can fully meet the needs of routine testing of pesticide residues. The experiment also examined the detection of pesticides below 10.0 μg/kg. For some pesticides, satisfactory results can be obtained even at very low concentrations of 0.1 μg/kg. As shown in Figure 9. This experiment is mainly based on the accurate quality information of pesticide compounds to carry out pesticide residue screening. Therefore, Database is required to study the basic screening limits. The matrix standards of 0.1, 0.5, 1.0, 10.0, 20.0, 50.0 μg/kg (435 pesticides) were prepared from apple and cucumber blank samples for determination. The screening results were used to perform Targeted Screening on the measurement results, and the pesticides in the two substrates of apple and cucumber were counted. The results showed that at the concentration of 1.0 μg/kg and below, the proportion of pesticides detected was 92.4% and 93.6%, respectively (see Figure 10). It can be seen that more than 100% of the pesticides can be qualitatively detected under the standard (10.0 μg/kg). The sensitivity of the method can fully meet the needs of routine testing of pesticide residues, and most pesticides can still be detected at lower concentrations. . 4. Conclusions <br>This experiment used Q Exactive-GC ultra-high resolution, stable mass accuracy and high sensitivity combined with TraceFinder software to create an accurate mass database of 435 pesticide compounds, using the exact mass and retention time of the compound. Information such as isotope strength and isotope distribution are combined to quickly screen agricultural product samples of different matrices. In the experiment, the resolution of the instrument was selected to a minimum of 60,000 FWHM (200 m/z) to improve the reliability of the test results, and at the same time reduce the cumbersome judgment caused by excessive false positives, thus speeding up the screening speed and convenience. At this resolution, the screening sensitivity can reach 10.0 μg/kg or less, which can fully meet the needs of routine testing of pesticide residues. references Electronic Lock Safe Box,Home Security Electronic Lock Box,Electronic Key Safes,Electronic Lock Hebei Tiger Brand Group Jia Bao Cabinet Industry Co. LTD , https://www.cntigersafe.com
1. Thermo Fisher Scientific (China) Co., Ltd.; 2. Thermo Fisher Scientifc, Liverpool, UK
Key words Q Exactive-GC; accurate quality database; pesticide residue
1. INTRODUCTION <br> Agricultural products are essential foods in people's daily lives. Their daily consumption and market demand are huge. At present, more than 1,100 pesticides are used in agricultural production worldwide [1]. In order to improve the output of agricultural products and improve their quality, the application of pesticides is inevitable, coupled with the abuse and misuse of pesticides, which not only makes pesticide residues in fruits and vegetables exceed the standard, but also aggravates the pollution of pesticides to the environment, and at the same time, on international trade and consumer health. Causes adverse effects. In response to this problem, many countries and international organizations have issued maximum residue limits (MRLs) for pesticides, which have strict regulations on different pesticide residues in different matrices [2]. China's GB2763-2014 "Maximum Residue Limits of Pesticide in Food" also stipulates 3,650 MRLs of 387 pesticides (GB 2763-2014) [3]. The problem of pesticide residues in fruits and vegetables has not only become a serious challenge in the field of food safety, but also restricts the import and export trade of fruit and vegetable products in China.
The trace multi-residue detection of pesticides has always been the research focus and development trend of pesticide residue analysis, and is the goal pursued by analytical chemists. At present, the world's pesticides plus its metabolites, isomers and degradation products can reach thousands, which determines the complexity and diversity of pesticide analysis. The rapid and accurate pesticide multi-residue detection method has become a key research direction at home and abroad.
At present, the commonly used pesticide residue screening is mostly realized by serial temperament or serial liquid quality detection. Tandem mass spectrometry is widely used in multi-residue analysis of foods and agricultural products because of its high sensitivity and specificity. However, as sample matrices become more complex, the number of pesticides detected increases, and the requirements for trace analysis, triple quadrupole mass spectrometry generally uses a multi-reaction monitoring (MRM) scan mode, with a fixed target compound, with a certain limitation. Quadrupole-time-of-flight mass spectrometry (Q-TOF) and electrostatic field orbitrap high-resolution mass spectrometry (Orbitrap) use a high-resolution full-scan approach (unrestricted target compound) to largely compensate for this defect and is widely used. Rapid screening of pesticide residues.
For high resolution selectivity, only when the resolution is higher than 50,000, the selectivity of the high resolution full scan mode will be better than the scan mode of the triple quadrupole mass spectrometer MRM, ie the intersection [4]. Therefore, during the sample screening analysis, Q Exactive-GC high-resolution mass spectrometry parameters have a resolution of 60,000 (m/z 200) or more, which greatly improves the speed of qualitative screening of pesticide residues and the reliability of results, while obtaining more Accurate quantitative results.
Q Exactive - GC, a temperament high-resolution product based on the unique high-resolution and high-quality precision measurement principle of Orbitrap electrostatic field orbital technology and excellent stability and operability, with resolutions up to 120,000 FWHM (200 m/z) ) while maintaining good sensitivity. Eliminating its full scan and high scanning speed, eliminating the need to limit the number of compounds, thereby achieving the goal of simultaneous screening of a large number of pesticides, and meeting the detection of low concentrations of pesticide residues in complex matrices and providing (for other components in the sample) retrospective the study. Not only that, Orbitrap combines the precise mass of the compound with retention time, isotope strength, isotopic distribution, etc. to achieve rapid and accurate screening of pesticides.
Based on Thermo Fisher Scientific's latest temperament high-resolution product, this study established 435 pesticide compound accurate mass database, which can complete sample data collection and pesticide unknown screening in 35 minutes. It has high sensitivity, good resolution and specificity. Strong, reproducible and so on. Good results have been obtained in the detection of pesticide residues in common fruits and vegetables.
2. Experimental part
2.1 Instruments and methods
2.1.1 Gas phase conditions Instrument model: Thermo Scientific TM TRACE 1310 GC
Injection volume: 1.0 μL
Lining: PTV splitless injection No split time: 1 min
Carrier gas: helium, 1.2 mL/min
Column oven temperature program: initial temperature 40 °C, hold 1.5 min; rise to 90 °C at 25 °C/min for 1.5 min; increase to 180 °C at 25 °C/min for 0 min; 5 °C/min rise to 280 °C, hold 0 min; 10 °C/min rise to 300 °C for 3 min.
2.1.2 Mass Spectrometry Conditions Instrument Model: Thermo Scientific TM Q Exactive-GC Mass Spectrometer Transmission Line: 250 °C
Ionization type: EI
Ion source: 280 °C
Electronic energy: 70 eV
Acquisition mode: high resolution full scan (FullScan)
Mass resolution: 60,000 FWHM (200 m/z)
Scanning range: 50-700 m/z
2.2 Sample preparation method:
1. Fruit and vegetable samples are based on "GCT 23206-2008 Determination of 512 pesticides and related chemical residues in fruit and vegetable juices and fruit wines by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry", with n-hexane as the volumetric solution [5].
3. Experiments and results
3.1 Qualitative capacity of high-resolution mass spectrometry <br> According to EU methodological standards, the mass spectrometry method must meet the requirements of four qualitative points [6]. For triple quadrupoles, only two pairs of parent and daughter ions are usually detected. The qualitative point is usually only 4-5; for high-resolution mass spectrometry, because it performs full scan measurement on the exact mass, each ion is defined as 2 qualitative points, and the relative abundance is more than 10% of the base peak. Ions can be used as a qualifier ion. Therefore, according to the above rules, the data collected by Q Exactive-GC has more than four qualitative points, and the library search of the full scan map can be realized. There is a strong advantage in the quasi-determinism of the compound.
3.2 Instrument performance
3.2.1 Scanning speed Normally, the peak width of the pesticide is between 3 and 10 s (depending on the position and concentration of the chromatographic peak). Each peak must meet at least 8-10 scan points to ensure the accuracy of data collection.
Q Exactive-GC still achieves an acquisition rate of 7.0 spectrum/s or more at 60,000 resolution, allowing the data to acquire enough scan points. At the same time, it is more important that the quality accuracy of each scan point can be kept within 1.0 ppm, which ensures the stability and reliability of the data. As shown in Figure 1.
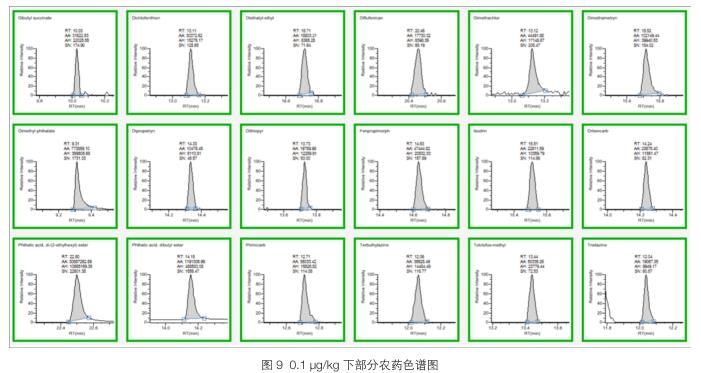
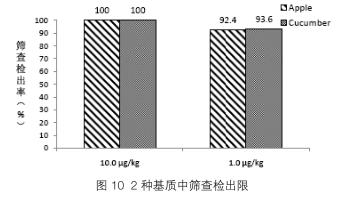
3.2.2 Quality Accuracy and Stability The ultra-high resolution makes the advantage of the accurate mass measurement of the instrument perfect, which is beneficial to the qualitative and quantitative determination of unknown compounds. However, the determination of the exact mass will be affected by factors such as matrix interference, compound concentration, instrument state, external environment, etc., to ensure a lower accurate mass deviation, in order to make the qualitative confirmation more. In the experiment, 1345 fragment ions were measured, and the mass deviation between the measured value and the theoretical value was within 1 ppm, as shown in Figure 2. The results show that Q Exactive-GC maintains good quality deviation during a large number of data acquisition processes, resulting in higher reliability.
The experiment also explored the mass accuracy of each collection point of the compound. In each collection point of the compound Chlorpyrifos, the mass deviation of the fragment ions (196.91964) can be kept within 0.5 ppm, as shown in Figure 3. Q Exactive-GC maintains good mass accuracy during every scan. 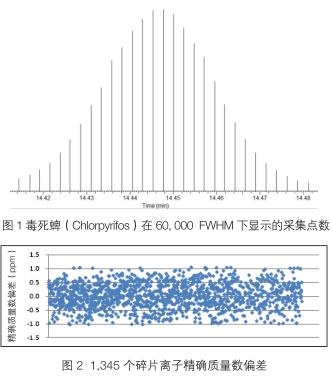


In this experiment, the isotope distribution and isotope abundance information of compounds have an important contribution in the retrieval score, which is an important parameter and judgment basis for screening . TraceFinder automatically generates the corresponding isotope peak theory information based on the chemical formula of the ion and automatically compares it with the measured value. Taking the pesticide herbicide (Nitrofen) as an example, the base peak ion chemical formula is C 12 Cl 2 H 7 NO 3 , and each accurate mass and its abundance ratio of the isotope peak clusters are actually matched with the theoretical values. As shown in Figure 7. 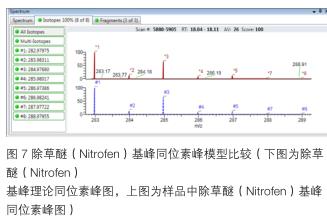
In the actual sample, at the concentration of 10.0 μg/kg, all compounds have good peak shapes, and the fragment ions can be detected and the ion ratios are highly matched. As shown in Figure 8. 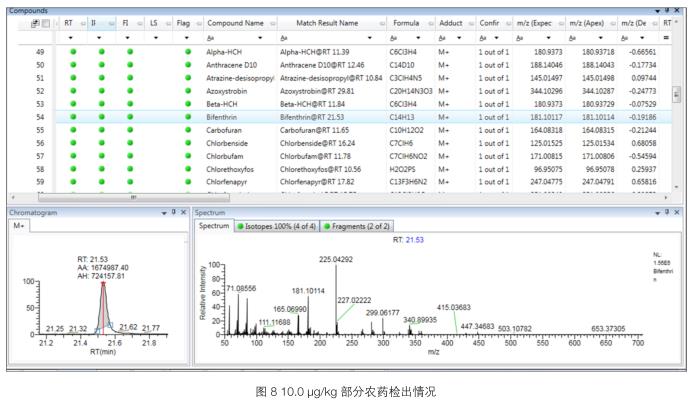
[1]. http://
[2]. http: / /
[3]. GB2763-2014 "Maximum Residue Limits of Pesticide in Foods"
[4]. Comprehensive comparison of liquid chromatography selectivity as provided by two types of liquid chromatography detectors (high resolution mass spectrometry and tandem mass spectrometry): "Where is the crossover point?" A. Kaufmann et al. / Analytica Chimica Acta 673 ( 2010) 60–72
[5]. GBT 23206-2008 "Determination of 512 pesticides and related chemical residues in fruit and vegetable juices and fruit wines by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry"
[6]. EC 657-2002